Dr Rebecca Wyten
Mastopexy surgery, with or without breast implants, is a cosmetic surgery procedure to adjust the positioning of the breasts.
This operation is performed under general anaesthesia. A nerve block (PECS II block) using local anaesthetic medication is also performed by your Specialist Anaesthetist before the operation starts to provide additional pain relief both during and after your operation.
Dr Wyten’s technique for this surgery is dependent on the needs of the individual patient and your breast shape, size and position. This procedure may require some removal of breast tissue or predominantly removal of excessive skin. Breast implants can also be inserted if a larger breast size is desired, as well as modifying breast positioning. Breast implants can be placed above or under the pectoralis muscle, depending on the type of implant used and the desired look.
This procedure typically takes approximately 2-3 hours to perform in the operating theatre, and an overnight stay in the hospital is usually required.
Mastopexy surgery alters the position and shape of your breasts, as well as the size if desired, and can offer the following:
It is important to have realistic expectations about what can be achieved with this surgery. You should also consider your natural breast size and shape and what will suit your overall body physique.
It is also important to be in good physical and mental health and be a non-smoker to reduce your risk of complications during and after surgery. If you are considering having mastopexy surgery, it is now an Australian requirement that you have a consultation with a General Practitioner (GP) or other specialist medical practitioner first to discuss your health and for an appropriate referral to a surgeon.
Dr Wyten uses Motiva and Mentor brand implants.
During your consultation with Dr Wyten, she will help you choose the most suited implants for your desired outcome by considering the following options:
It is recommended that patients take one to two weeks off work and strenuous home duties following Mastopexy surgery. It is important to follow the instructions given during your recovery, including when you can resume driving and exercise. It may be necessary to get additional support for childcare, pet care, and other activities around the home during your recovery, as you will be unable to do any lifting.
It is typical to have some discomfort after mastopexy surgery. You will be given instructions after your surgery on how to manage this in the first couple of weeks after surgery. You will also need to wear supportive undergarments, and Dr Wyten’s preferred supportive post-surgical bras will be provided after your surgery. You may wish to purchase some additional post-surgical bras for your recovery.
All surgeries have risks, including scarring, bleeding, blood clots (deep vein thromboses and pulmonary emboli) and infection. There are also risks associated with a general anaesthetic.
Dr Wyten will discuss risks specific to this surgery with you during your consultation. Written information will also be provided for you to read before you proceed with surgery. Some risks associated with this procedure include:
If you experience any unusual pain, swelling or bleeding after surgery, please seek help immediately.
If you are considering this type of surgery, it is important to choose a Specialist Plastic Surgeon that has extensive training and is an experienced medical professional.
These before and after photographs are of patients of Dr Rebecca Wyten who have given consent for the sharing of their photos.
Individual results may vary, and your outcomes may be different to these photos.
24 months since surgery
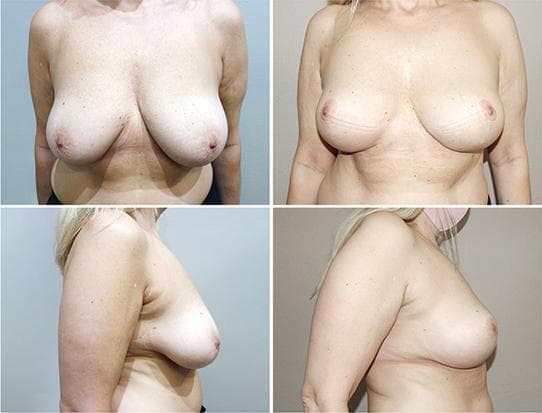
1 month since surgery
400cc High Profile to 350cc High Profile
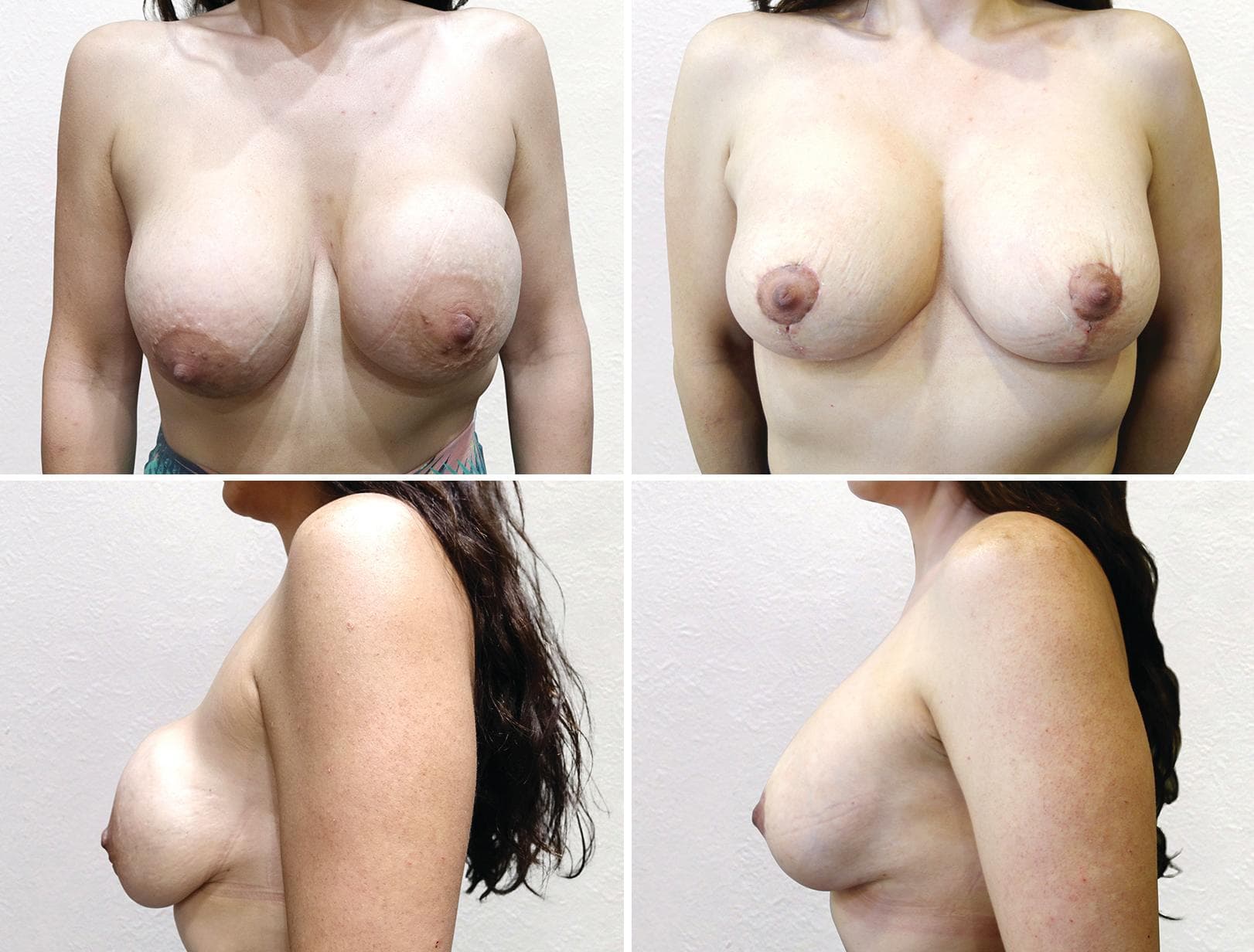
9 months since surgery
300cc
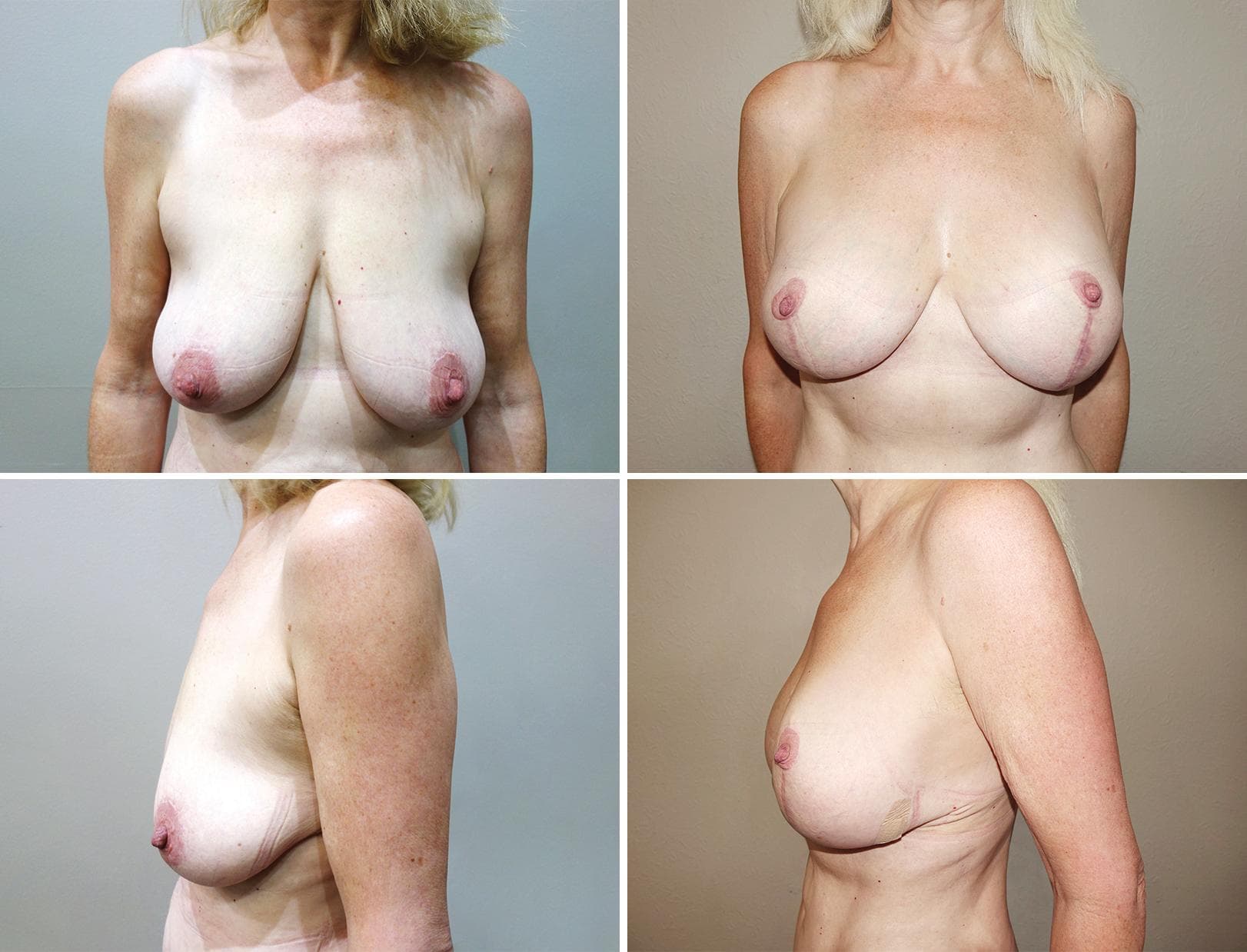
24mths post surgery
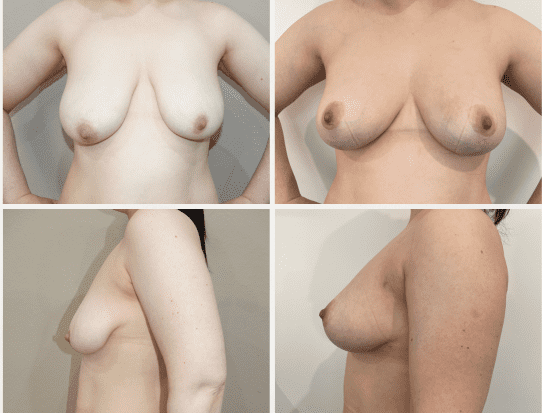
12 months post surgery
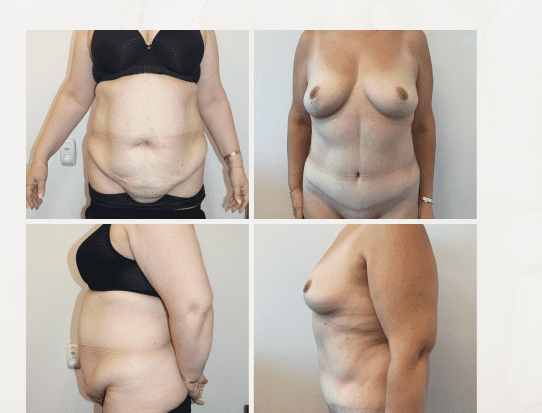
7 months post surgery
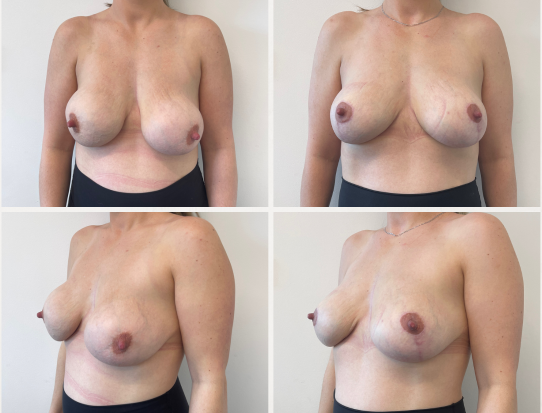
12 months post surgery
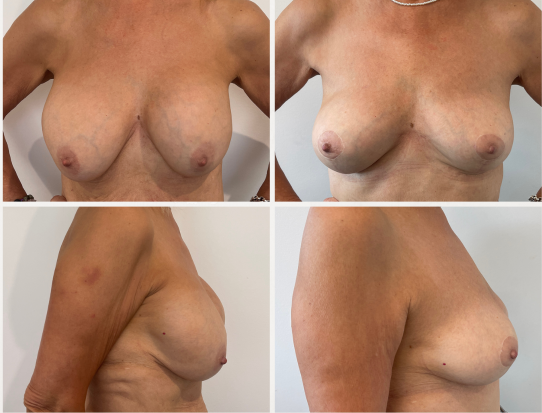
12 months post surgery
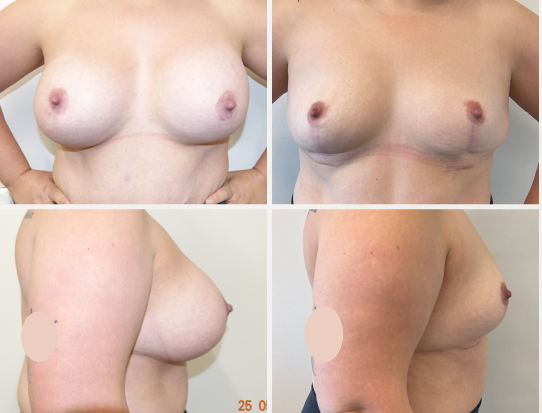
Q. How long does a breast lift without implants last?
Mastopexy (breast lift) results without implants can be long-lasting, typically lasting 10 to 15 years or more, depending on factors like ageing, natural skin elasticity, weight fluctuations and pregnancy. However, over time, natural changes in the breast tissue may occur, and some patients may choose to have additional procedures to maintain the results.
Q. What is a breast reduction and breast lift surgery?
A combined reduction mammaplasty and Mastopexy removes excess breast tissue, fat, and skin to reduce breast size while lifting the remaining tissue. This procedure may alleviate symptoms like back and neck pain and alter the breast and/ or nipple position.
Q. What is the difference between a mastopexy (breast lift) with implants and mastopexy (breast lift) without implants?
Mastopexy with implants involves both a breast lift procedure and the addition of implants to alter the breast size or shape. In contrast, Mastopexy without implants focuses solely on repositioning and reshaping the breast tissue to alter the appearance of the breasts without the use of implants.
Q. What are the incision types for mastopexy (breast lift) surgery?
Different surgeons may use different types of mastopexy (breast lift) techniques, and each patient will be assessed for suitability for a surgical technique depending on the outcome that is required. Below are some of the more common types of techniques used.
1. Periareolar Incision (Donut Lift)
This incision is made around the areola in a circular pattern. It’s best It is optimal for cases where only a small amount of lift is needed. The scar is hidden around the areola, making it less noticeable. It can also be used to reduce the size of the areola if desired. This option can be suitable for those requiring minimal breast changes.
2. Vertical Incision (Lollipop Lift)
The vertical incision is made around the areola and extends downward toward the breast crease, forming a “lollipop” shape. It can be suitable for patients needing lifting and reshaping. While the scar will be visible as a vertical line down the centre of the breast, it often fades over time. This incision offers a balance of results with relatively minimal scarring compared to the anchor incision.
3. Inverted T Incision (Anchor Lift)
The inverted T incision involves three cuts: around the areola, vertically down to the breast fold, and horizontally along the breast crease. It can provide the most control over reshaping and repositioning the breast tissue. Although the scars are more visible, this incision allows for more extensive adjustments and is commonly used for those with larger breasts or more significant tissue changes.
4. Hidden Scar Mastopexy
The hidden scar mastopexy focuses on minimising visible scarring by placing the incision only around the areola or in the breast crease. It’s suitable for those who need request a subtle lift. This technique leaves fewer visible scars but is not ideal for more extensive adjustments. It’s a good option for patients with less pronounced changes in breast shape.
Q. Is a mastopexy covered by Medicare?
In Australia, Medicare may cover some of the costs of a mastopexy (breast lift) under certain circumstances, but it is typically only partially covered if the surgery is deemed medically necessary.
Medicare may partially cover the procedure if there is a medical reason for the breast lift, such as:
For purely aesthetic reasons, mastopexy is not covered by Medicare.
If you believe that you may qualify for a Medicare coverage rebate, your GP and surgeon will assess your situation. They will provide appropriate documentation if required and determine if the procedure meets the necessary medical criteria for a Medicare claim.
It’s also advisable to check with your private health insurance provider, as they may cover part of the procedure if it’s considered medically necessary and you have the right level of cover.
Q. What is glandular ptosis?
Glandular ptosis refers to the downward movement of the glandular tissue within the breast. The glandular tissue is the part of the breast responsible for milk production, and when it experiences ptosis, it can cause the breast to appear lower or more elongated.
This can occur as a result of aging, pregnancy, weight fluctuations or other factors that impact the elasticity of the breast skin and tissue. Unlike general ptosis, which often involves the skin and soft tissue, glandular ptosis specifically focuses on the position of the glandular tissue itself.
In breast surgery, particularly during a mastopexy (breast lift) or breast augmentation, glandular ptosis may be addressed by repositioning both the glandular tissue and the surrounding skin.
Q. What is breast ptosis?
In the context of mastopexy surgery, breast ptosis refers to the descent or positioning of the breasts. This can occur due to various factors, including the natural process of ageing, pregnancy, weight changes or genetics.
During a mastopexy procedure, excess skin is removed, and the breast tissue is repositioned. Depending on an individual’s anatomy, the procedure can also elevate the nipple and areola.
Q. What is the difference between a mastopexy and a breast lift?
Mastopexy and breast lift refer to the same surgical procedure. Mastopexy is the medical term for the procedure, while breast lift is the more commonly used term in everyday language. Both terms describe a surgery designed to alter the position of breasts by removing excess skin and repositioning the breast tissue.
Q. Can I breastfeed after mastopexy surgery?
Breast surgery may affect your ability to breastfeed. Certain techniques can reduce the risk of not being able to breastfeed after this surgery, but the outcome of any surgery cannot be guaranteed.
Q. How long do breast implants last for?
It is generally recommended that breast implants be changed after 10 years, although they may last longer in some individuals. Complications or issues can arise at any time after surgery, including rupture, leakage or capsular contracture, which can alter the appearance or cause discomfort. In these cases, implants may need to be removed or replaced.
There are also times in which clients’ personal preference for the size or shape of their implant may change over time, and naturally occurring changes to the body and breasts over time.
Q. What are the scars like after mastopexy surgery?
It is important to follow the postoperative instructions you’re given after surgery to assist with maturing scarring, which will ultimately affect the appearance of your scars. With mastopexy surgery performed by Dr Wyten, you will commonly have a scar around the nipple-areola and a scar vertically below the nipple.
In cases where there is excess skin to remove, you may also have an ‘anchor’ scar underneath the breast. Scars typically take up to 1 to 2 years to completely mature. Mastopexy (breast lift) recovery time and scarring will be different for each patient, depending on the procedure, general health, lifestyle, skin type and postoperative care.
Q. What results can be achieved with mastopexy surgery?
Mastopexy surgery is performed to modify the position and shape of the breasts and nipples. The size of the breasts can also be reduced or increased (using breast implants or fat grafting) with this surgery. Existing asymmetry of the breasts may also be reduced. Your final result following mastopexy surgery is dependent on a number of factors, including:
Dr Wyten will discuss all of these factors with you during your consultation.